
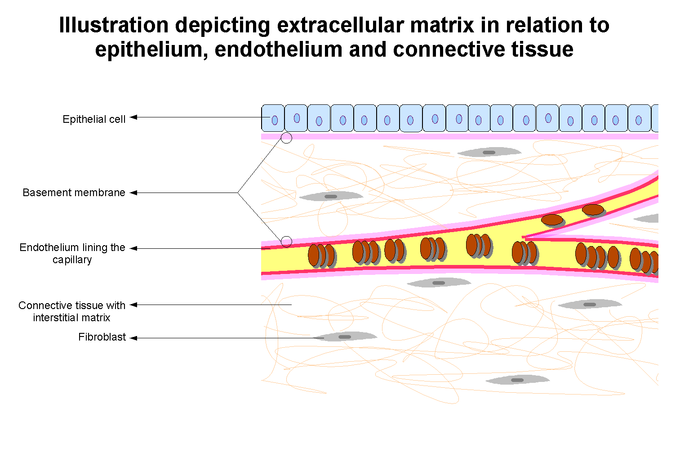
To calculate the intracellular fluid volume subtract the extracellular fluid volume from the total fluid volume. To calculate the interstitial (fluid not in the cells and not in the blood) fluid volume, subtract the plasma volume from the extracellular volume. To measure the extracellular fluid volume, use a cell inpermeant marker substance such as inulin or mannitol that will equilibrate everywhere except in the cells (it is possible to make inulin and mannitol radioactive). One such marker is Evan's Blue, a dye which binds to plasma proteins. Therefore, to measure the volume of the blood plasma fluid compartment, you need a marker which equilibrates throughout the blood supply and nowhere else. M U is usually calculated from C U, the concentration of marker lost in the urine and V U, the volume of the urine thus: M U = C U. Where V is the volume of the body fluid compartment, M is the mass of marker injected, M U is the mass of marker lost in the urine during equilibration and C is the measured concentration of the marker. As this is not possible (the kidney will excrete everything dissolved in the bloodstream) the calculation must correct for excretion. To be an absolutely perfect marker, the substance should also not be excreted. Therefore: if you know the mass of marker injected into the body and are able to measure the marker concentration once equilibration is complete, you can calculate the volume of the compartment occupied by the marker. Plasma is the fluid circulating in the blood vessels and is the smaller of the. When fibroblasts are cultured in vitro in a collagen gel, the fibroblasts attach to the collagen fibers and, by exerting tension on those attachments, reduce gel volume ( 11 ). Given that concentration (C) = mass (M) / volume (V) it should be obvious that: ECF is further divided into two compartments: plasma and interstitial fluid. These interstitial structural elements make distinct mechanical contributions to the relationship between interstitial volume and interstitial fluid pressure. Furthermore, it must be possible to measure the concentration of the marker once equilibration is complete.Tritiated ( 3H) water is a good marker for the whole body fluid compartment because it diffuses throughout the body, it is chemically identical to normal water and it is easy to measure the equilibrium concentration because 3H water is radioactive. 1.8K 150K views 5 years ago Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology In this video we discuss what is the extracellular matrix and what is interstitial fluid. To be a perfect marker a substance must also not be metabolised. of these cations between the cytosol and the interstitial fluid. To measure the volume of any fluid compartment within the body you must inject or infuse a marker substance that will equilibrate (diffuse freely to a uniform concentration) throughout this compartment. Thus, Na+ is more concentrated in the extracellular fluids than in the cytosol, and the. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules that can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Body fluid compartments calculations Body Fluid compartments Measuring Body Fluid Compartments The concentrations of ions, such as sodium and potassium, are generally lower in the cytosol compared to the extracellular fluid these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation and signal transduction. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, it mainly functions as a fluid medium for intracellular signaling (signal transduction ) within the cell, and plays a role in determining cell size and shape. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. The cytosol includes dissolved molecules and water. The cytosol: The cytosol (11) is the fluid within the plasma membrane of a cell and contains the organelles. The contents of a eukaryotic cell within the cell membrane, excluding the cell nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles (e.g., mitochondria, plastides, lumen of endoplasmic reticulum, etc.), is referred to as the cytoplasm. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments. It is separated into compartments by membranes that encircle the various organelles of the cell.
The intracellular fluid of the cytosol or intracellular fluid (or cytoplasm ) is the fluid found inside cells.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
